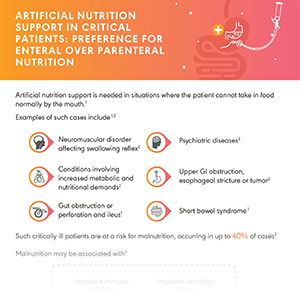
Critically ill patients are at a risk for malnutrition, occurring in up to 40% of the cases, thus requiring nutritional support.
Knowledge Library
OVERCOMING CHALLENGES TO LONG-TERM FEEDING
Enteral feeding is an important technique to deliver nutrition to patients who cannot take in food normally by the mouth. However, it can be associated with various challenges and complications. Explore any of the topics below and download infographics on ways of overcoming some associated challenges.

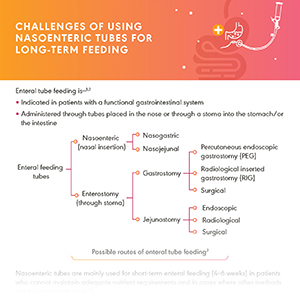
Types of Feeding Tubes for Long-Term Enteral Nutrition
NICE guidelines 2020 recommend gastrostomy feeding in patients likely to need long term (more than 4 weeks) enteral tube feeding. Balloon gastrostomy tubes must be used even as replacement tubes, instead of Foley catheters, whose long-term use comes with several complications.
Types and Placement of Feeding Tubes
The pull technique for tube placement has reported 30%-50% complication rates in head and neck cancer patients.
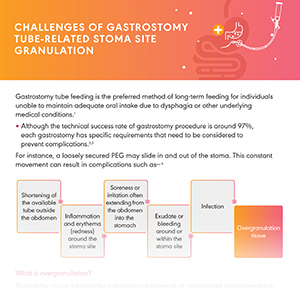
Enteral Feeding Complications
Replacement of the Foley catheter with a gastrostomy tube containing an external retention device, or a gastrostomy button may help resolve the problem of tube migration. Presence of overgranulation tissue, although not life threatening, can severely affect the patient’s quality of life.

Postpyloric Feeding
Postpyloric feeding through percutaneous endoscopic gastrojejunostomy (PEG-J) helps circumvent the gastric passage and improves the drainage of gastric secretions via decompression holes.

Home Enteral Nutrition
Home enteral nutrition helps improve clinical outcomes and reduce the incidence of infectious complications and the number of hospital admissions.
SHORT-TERM FEEDING TUBE PLACEMENT IN CRITICAL CARE
Malnutrition affects both patient outcomes and hospital resources.
1. Nutritional support is essential and can be either through dietary supplementation or artificial nutrition, enteral (EN) or parenteral (PN).
2. In hospitalized patients, guidelines recommend using a naso gastric (NG) tube as an initial access device for EN.
3. Post pyloric tubes [nasointestinal (NI) tubes] may be opted in case of gastric feeding intolerance.
Explore any of the topics below and download infographics on ways of overcoming some associated challenges.

Nutrition in Critically Ill patients
Malnutrition—a debilitating and highly prevalent condition in the hospital setting, with a prevalence ranging from 13%–88% depending on the patient population, disease severity, and the criteria used to identify its occurrence.

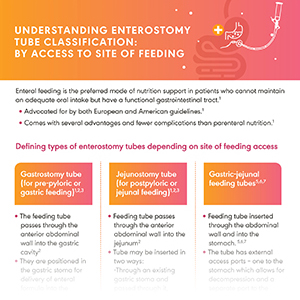
Considerations for Choosing and Placing a Feeding Tube
Enteral access provides means for short-term or long-term delivery of nutrition into the GI tract of patients who cannot maintain adequate nutrient requirements. There are several critical components to consider for selection of Enteral Access Devices and several methods for nasogastric/nasointestinal (NG/NI) enteral access. Selection of an appropriate enteral access device is based on the patient’s GI anatomy and function, accessibility, disease state, and expected duration of therapy.

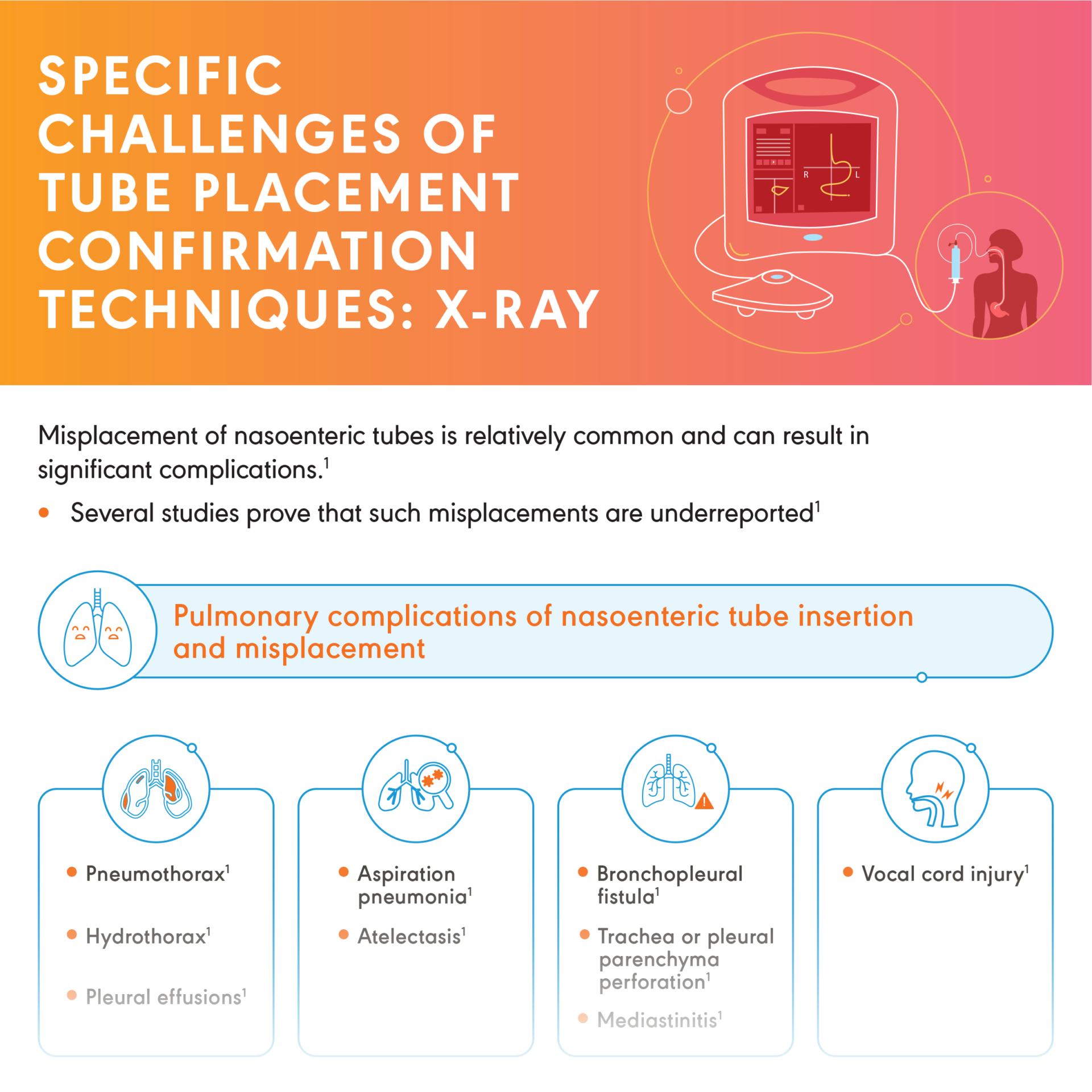
Challenges with Nasoenteric Tubes in Hospitalized Patients
Clogged enteral feeding tubes and accidental dislodgments are a significant barrier to effective nutrition delivery, hydration and medication to patients who cannot tolerate oral intake.

Feeding Tube Placement Considerations in Specific Patient Profiles
Feeding tube placements considerations in specific patient types suffering from Gastroparesis and Stroke.
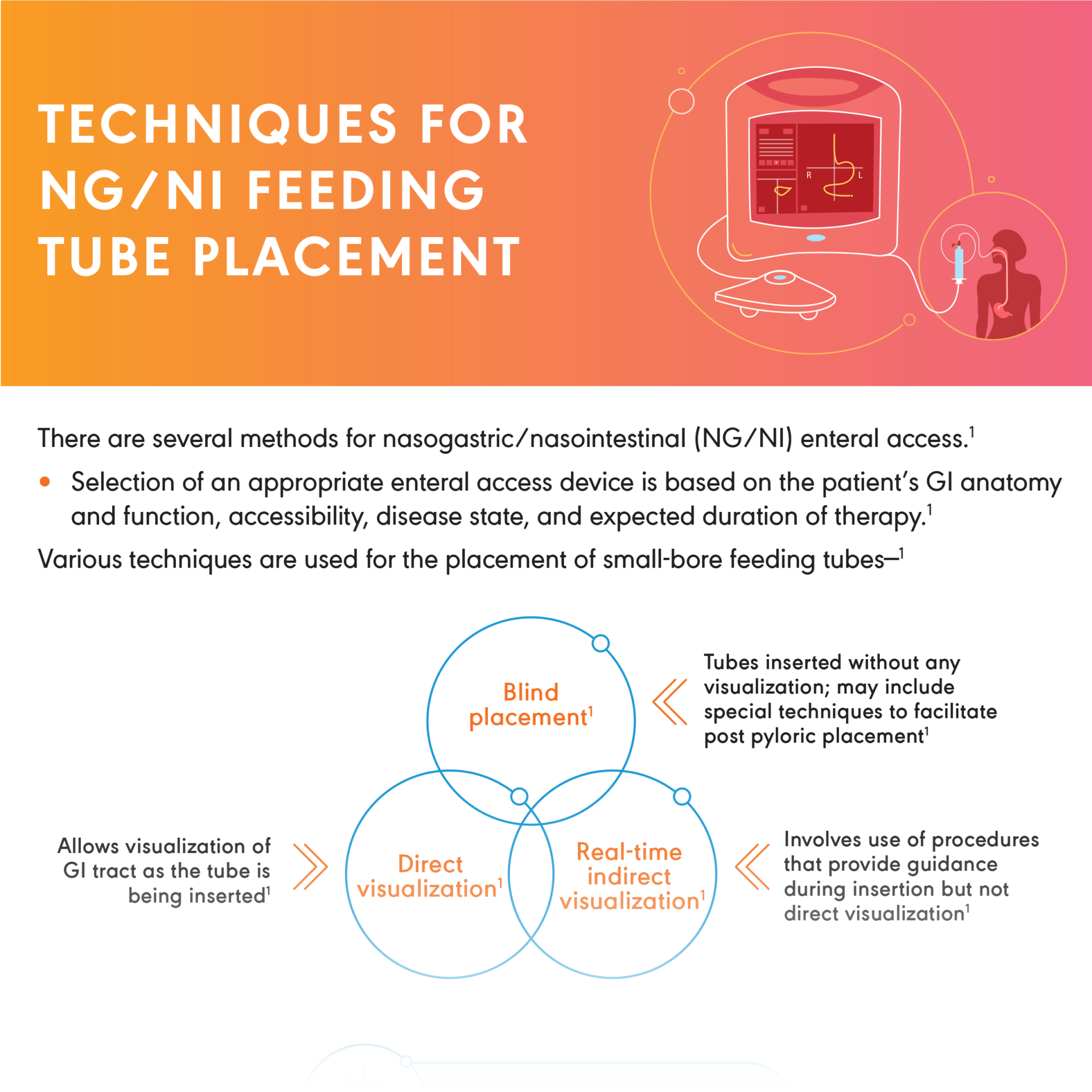
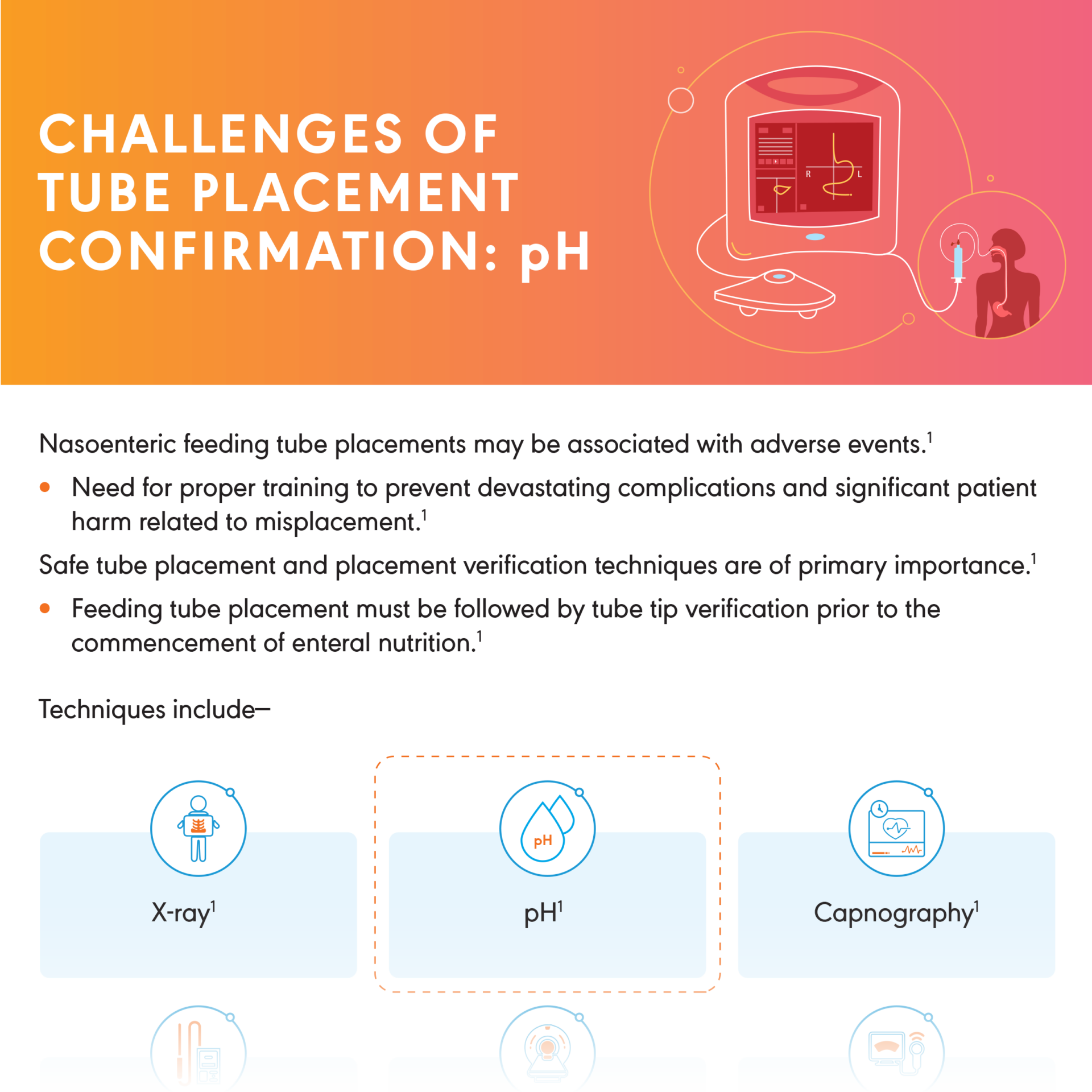
Nasoenteric Feeding Tube Placement Confirmation Techniques
Insertion of a nasoenteric tube is not always successful. Misplacement is common. Methods used to confirm feeding tube tip location and
associated limitations can vary.

Cortrak*EAS: To Guide Safer Feeding Tube Placement
A single error at the time of nasogastric and/or nasoenteric tube placement may lead to complications. On-screen visualization at bedside supports qualified clinicians in placing feeding tubes, confirming placement per institution protocol and reducing secondary insertion attempts.
SHORT-TERM FEEDING INFOGRAPHICS
Nutrition in Critically Ill patients
Considerations for Choosing and Placing a Feeding Tube
Challenges with Nasoenteric Tubes in Hospitalized Patients
FEEDING TUBE PLACEMENT CONSIDERATIONS IN SPECIFIC PATIENT PROFILES
Nasoenteric Feeding Tube Placement Confirmation Techniques
CORTRAK*EAS: TO GUIDE SAFER FEEDING TUBE PLACEMENT
Adult Airway Management and ETT Design
Pediatric Airway Management and ETT Design
Managing Accumulated Secretions with Closed Suctioning
Managing Accumulated Secretions with Subglottic Suctioning
PROTECT. PROVIDE. BREATHE.
Patients with serious respiratory conditions deserve quality respiratory medical device solutions whether at home or in the hospital. Explore any of the topics below and download infographics that discuss how our innovative respiratory solutions can help overcome any associated challenges these patients may face.

Adult Airway Management and ETT Design
Up to 88% of intubated critically ill patients suffer from microaspiration and VAE. Other complications like tracheal trauma may also occur due to improper endotracheal tube design. Innovations in endotracheal tube cuff material, shape and length may reduce risks such as microaspiration and VAE.

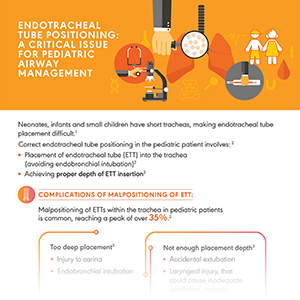
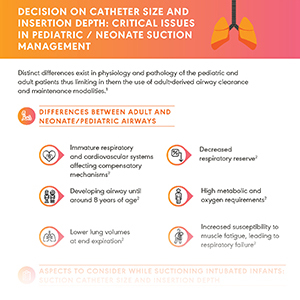
Pediatric Airway Management and ETT Design
A study found that rate of reintubation required with uncuffed tubes is 30% in children <2 years and 18% in
patients ≥2 years. Use of traditional uncuffed tubes, poorly designed cuffed tubes or any malpositioning of tubes may pose respiratory, post-extubation as well as economic and environmental complications.

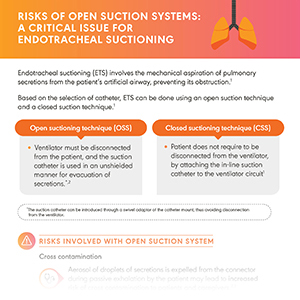
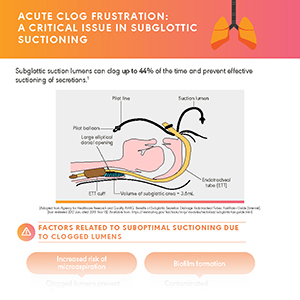
Managing Accumulated Secretions with Closed Suctioning
Disrupted physiology of the respiratory system leading to microaspiration, tracheobronchial colonization and VAP—is it a result of accumulated airway secretions? Open suction systems pose a 3.5X greater risk of VAP as compared to closed suction systems.
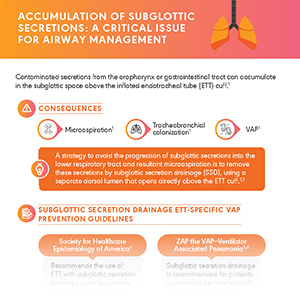
Managing Accumulated Secretions with Subglottic Suctioning
Studies prove that the use of subglottic secretion drainage reduces VAP occurrence with a relative risk reduction of 45%.